How Probiotics Can Promote Better Mental Health
The concept of maintaining a healthy gut for overall physical wellness isn't new, but recent research suggests that it might be even more significant than we previously thought. It's now believed that our digestive system, often referred to as our "second brain," plays a critical role in regulating not just our physical health but our mental health as well. A key part of this relationship involves probiotics—beneficial bacteria that reside in our gut. Let's explore how these microscopic organisms might hold the key to better mental health.
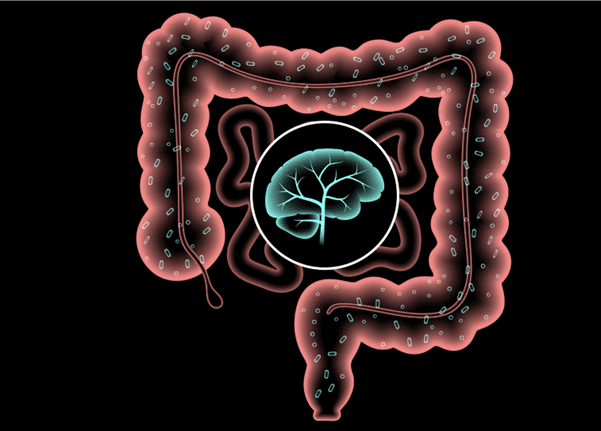
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Two-Way Street
The communication network that connects the gut and the brain is known as the gut-brain axis (GBA). This complex system involves multiple pathways, including the nervous system, hormones, and the immune system. Information flows in both directions, allowing the brain to influence gut function and vice versa. This bidirectional communication is why stress can lead to digestive issues and why gastrointestinal problems might exacerbate stress or anxiety.